课题组在《Applied Surface Science》发表光催化固氮文章,题目为“Enhancing Photocatalytic Nitrogen Fixation Performance of Co-doped Bismuth Molybdate through Band Engineering Tuning”,第一作者是2021级博士研究生刘振宇同学,通讯作者是李晓曼副教授和罗民教授。
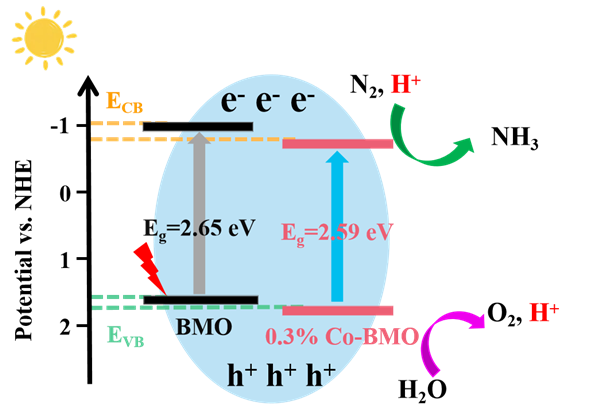
Abstract: Energy band engineering strategy by doping has been extensively proved to have great influence on photocatalytic properties of semiconductors. Herein, a novel Co-doped Bi2MoO6 (Co-BMO) photocatalyst was developed for photocatalytic nitrogen fixation. Co-BMO with microsphere structure was synthesized by a one-step solvothermal method. The NH3 yield of 0.3% Co-BMO (130.07 μmol·h-1·gcat-1) was about 3.9 times higher than that of pure BMO without scavengers and visible light irradiation. The band gap of 0.3% Co-BMO was reduced and the average PL lifetime was improved due to the successful doping of Co2+, which directly led to higher separation efficiency of photogenerated carriers and improved photocatalyst activity. In addition, gas chromatography (GC) tests showed that 0.3% Co-BMO had a higher photocatalytic oxygen production capacity, which meant that more protons would be involved in the nitrogen reduction reaction. Their synergistic effect greatly enhanced the photocatalytic nitrogen fixation ability of 0.3% Co-BMO. This novel photocatalyst may be a promising candidate for photocatalytic nitrogen fixation.